

The vecmatch package implements the Vector Matching
algorithm introduced in the paper Estimation of Causal Effects with
Multiple Treatments: A Review and New Ideas by Lopez and Gutman
(2017). This package allows users to:
You can install the latest version of vecmatch from GitHub with:
# Install devtools if its not already installed
if(!require(devtools)){
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
}
# Install the vecmatch package directly from github
devtools::install_github("Polymerase3/vecmatch")Once the package is released on CRAN, you can install it using the
standard workflow: install.packages("vecmatch").
The vecmatch package has an exact workflow and it is advisable to follow it. It consists of 5 steps and ensures the best possible matching quality using the vector matching algorithm:
Visualize covariate imbalances in your dataset using the
raincloud() function for continuous variables and the
mosaic() function for categorical variables. Both functions
support grouping by up to two categorical variables (group
and facet arguments) and provide standardized mean
differences and significance tests.
library(vecmatch)
raincloud(
data = cancer,
y = bmi,
group = status,
facet = sex,
significance = "t_test",
sig_label_color = TRUE,
sig_label_size = 3,
limits = c(7, 48)
)
#> Warning: Removed 9 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
#> (`geom_flat_violin()`).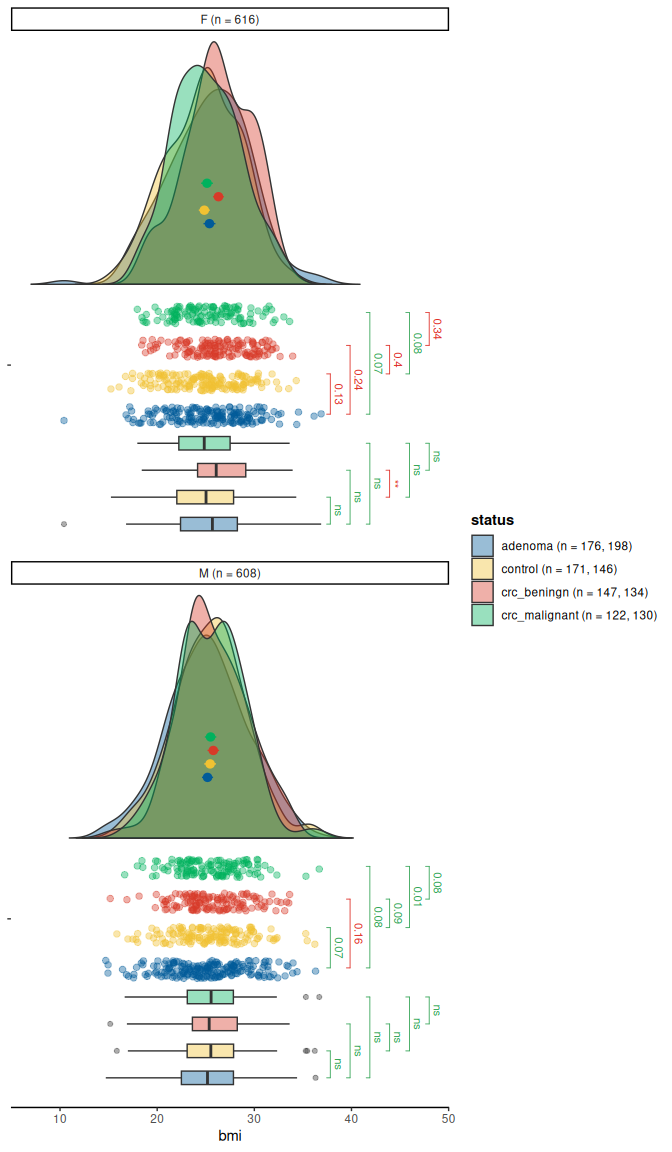
Next, estimate generalized propensity scores for the treatment
variable. These scores represent treatment assignment probabilities
based on user-defined covariates. Use the estimate_gps()
function to estimate GPS. As a result, a matrix of generalized
propensity scores is returned:
formula_cancer <- formula(status ~ bmi * sex)
gps_matrix <- estimate_gps(formula_cancer,
data = cancer,
method = "vglm",
reference = "control"
)
head(gps_matrix, n = 7)
#> treatment control adenoma crc_beningn crc_malignant
#> 1 control 0.3347396 0.2858184 0.1622951 0.2171469
#> 2 control 0.2397453 0.3487326 0.2006854 0.2108367
#> 3 control 0.2400506 0.2885477 0.2533414 0.2180602
#> 4 control 0.2478800 0.2856531 0.2783953 0.1880716
#> 5 control 0.2398759 0.2848793 0.2568960 0.2183489
#> 6 control 0.2652354 0.2878765 0.2518512 0.1950369
#> 7 control 0.2806189 0.2888866 0.2297684 0.2007260As you can see, each row in the resulting GPS matrix contains treatment assignment probabilities for all levels of the treatment variable, summing to 1.
The next step involves estimating the boundaries of the common
support region (CSR). The lower and upper CSR boundaries define the
range of propensity scores where observations are present across all
treatment groups. You can calculate these boundaries by applying the
csregion() function to the gps_matrix
object:
csr_matrix <- csregion(gps_matrix)
#>
#> Rectangular CSR Borders Evaluation
#> ==================================
#>
#> Treatment | Lower CSR limit | Upper CSR limit | Number excluded
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------
#> control | 0.1900629 | 0.3530295 | 27
#> adenoma | 0.2678156 | 0.3802609 | 20
#> crc_beningn | 0.1429038 | 0.3802038 | 27
#> crc_malignant | 0.1605948 | 0.2214335 | 27
#>
#> ===================================================
#> The total number of excluded observations is: 40
#> Note: You can view the summary of the CSR calculation using the `attr()` function.The csregion() function outputs a matrix of generalized
propensity scores, excluding any observations that fall outside the CSR.
Additionally, it provides a summary of the process in the console. You
can retrieve additional attributes of the csr_matrix object using the
attr() function. Details about these attributes can be
found in the documentation for csregion().
You can use the csr_matrix object to perform the actual
matching with the vector matching algorithm using the
match_gps() function. In this example, matching is
performed without replacement, using a larger caliper and a one-to-one
matching ratio:
matched_data <- match_gps(
csmatrix = csr_matrix,
reference = "control",
caliper = 1
)Finally, the quality of the matching process can be evaluated using
the balqual() function. This function provides both mean
and maximum values for various metrics, such as the standardized mean
difference, variance ratio, and r-effect size coefficient.
balqual(matched_data,
formula_cancer,
statistic = "max"
)
#>
#> Matching Quality Evaluation
#> ================================================================================
#>
#> Count table for the treatment variable:
#> --------------------------------------------------
#> Treatment | Before | After
#> --------------------------------------------------
#> adenoma | 355 | 147
#> control | 304 | 147
#> crc_beningn | 278 | 147
#> crc_malignant | 247 | 147
#> --------------------------------------------------
#>
#>
#> Matching summary statistics:
#> ----------------------------------------
#> Total n before matching: 1184
#> Total n after matching: 588
#> % of matched observations: 49.66 %
#> Total maximal SMD value: 0.023
#> Total maximal r value: 0.002
#> Total maximal Var value: 1.015
#>
#>
#> Maximal values :
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#> Variable | Coef | Before | After | Quality
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#> bmi | SMD | 0.259 | 0.023 | Balanced
#> bmi | r | 0.010 | 0.002 | Balanced
#> bmi | Var | 1.128 | 1.015 | Balanced
#> sexF | SMD | 0.153 | 0.000 | Balanced
#> sexF | r | 0.006 | 0.000 | Balanced
#> sexF | Var | 1.004 | 1.000 | Balanced
#> sexM | SMD | 0.153 | 0.000 | Balanced
#> sexM | r | 0.006 | 0.000 | Balanced
#> sexM | Var | 1.004 | 1.000 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexF | SMD | 0.151 | 0.006 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexF | r | 0.007 | 0.001 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexF | Var | 1.046 | 1.005 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexM | SMD | 0.151 | 0.003 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexM | r | 0.006 | 0.001 | Balanced
#> bmi:sexM | Var | 1.023 | 1.003 | Balanced
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------------------You can open the full documentation of the vecmatch package using:
help(package = vecmatch)