The JMH package jointly models both mean trajectory and
within-subject variability of the longitudinal biomarker together with
the (competing risks) survival outcome.
You can install the development version of JMH from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("shanpengli/JMH")The JMH package comes with several simulated datasets.
To fit a joint model, we use JMMLSM function.
library(JMH)
#> Loading required package: survival
#> Loading required package: nlme
#> Loading required package: MASS
#> Loading required package: statmod
data(ydata)
data(cdata)
## fit a joint model
fit <- JMMLSM(cdata = cdata, ydata = ydata,
long.formula = Y ~ Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time,
surv.formula = Surv(survtime, cmprsk) ~ var1 + var2 + var3,
variance.formula = ~ Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time,
quadpoint = 6, random = ~ 1|ID, print.para = FALSE)
fit
#>
#> Call:
#> JMMLSM(cdata = cdata, ydata = ydata, long.formula = Y ~ Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time, surv.formula = Surv(survtime, cmprsk) ~ var1 + var2 + var3, variance.formula = ~Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time, random = ~1 | ID, quadpoint = 6, print.para = FALSE)
#>
#> Data Summary:
#> Number of observations: 1353
#> Number of groups: 200
#>
#> Proportion of competing risks:
#> Risk 1 : 45.5 %
#> Risk 2 : 32.5 %
#>
#> Numerical intergration:
#> Method: adaptive Guass-Hermite quadrature
#> Number of quadrature points: 6
#>
#> Model Type: joint modeling of longitudinal continuous and competing risks data with the presence of intra-individual variability
#>
#> Model summary:
#> Longitudinal process: Mixed effects location scale model
#> Event process: cause-specific Cox proportional hazard model with non-parametric baseline hazard
#>
#> Loglikelihood: -3621.603
#>
#> Fixed effects in mean of longitudinal submodel: Y ~ Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time
#>
#> Estimate SE Z value p-val
#> (Intercept) 4.85342 0.12451 38.97918 0.0000
#> Z1 1.55235 0.16535 9.38841 0.0000
#> Z2 1.93774 0.14598 13.27409 0.0000
#> Z3 1.09289 0.05321 20.53796 0.0000
#> time 4.01129 0.02978 134.71376 0.0000
#>
#> Fixed effects in variance of longitudinal submodel: log(sigma^2) ~ Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + time
#>
#> Estimate SE Z value p-val
#> (Intercept) 0.50745 0.12838 3.95260 0.0001
#> Z1 0.50509 0.16005 3.15590 0.0016
#> Z2 -0.42508 0.13781 -3.08463 0.0020
#> Z3 0.14405 0.04494 3.20563 0.0013
#> time 0.09050 0.02422 3.73720 0.0002
#>
#> Survival sub-model fixed effects: Surv(survtime, cmprsk) ~ var1 + var2 + var3
#>
#> Estimate SE Z value p-val
#> var1_1 1.09710 0.32647 3.36051 0.0008
#> var2_1 0.19237 0.26154 0.73553 0.4620
#> var3_1 0.49611 0.08908 5.56951 0.0000
#>
#> var1_2 -0.88311 0.33702 -2.62037 0.0088
#> var2_2 0.80905 0.30127 2.68549 0.0072
#> var3_2 0.20871 0.09312 2.24143 0.0250
#>
#> Association parameters:
#> Estimate SE Z value p-val
#> (Intercept)_1 0.97480 0.62808 1.55202 0.1207
#> (Intercept)_2 -0.18580 0.47949 -0.38750 0.6984
#> var_(Intercept)_1 0.50030 0.58190 0.85977 0.3899
#> var_(Intercept)_2 -0.84481 0.52520 -1.60857 0.1077
#>
#>
#> Random effects:
#> Formula: ~1 | ID
#> Estimate SE Z value p-val
#> (Intercept) 0.49542 0.11339 4.36913 0.0000
#> var_(Intercept) 0.45581 0.11129 4.09578 0.0000
#> (Intercept):var_(Intercept) 0.26738 0.07854 3.40429 0.0007The JMH package can make dynamic prediction given the
longitudinal history information. Below is a toy example for competing
risks data. Conditional cumulative incidence probabilities for each
failure will be presented.
cnewdata <- cdata[cdata$ID %in% c(122, 152), ]
ynewdata <- ydata[ydata$ID %in% c(122, 152), ]
survfit <- survfitJMMLSM(fit, seed = 100, ynewdata = ynewdata, cnewdata = cnewdata,
u = seq(5.2, 7.2, by = 0.5), Last.time = "survtime",
obs.time = "time", method = "GH")
survfit
#>
#> Prediction of Conditional Probabilities of Event
#> based on the adaptive Guass-Hermite quadrature rule with 6 quadrature points
#> $`122`
#> times CIF1 CIF2
#> 1 5.069089 0.00000000 0.0000000
#> 2 5.200000 0.05596021 0.0000000
#> 3 5.700000 0.14584944 0.0000000
#> 4 6.200000 0.33882152 0.0000000
#> 5 6.700000 0.33882152 0.0000000
#> 6 7.200000 0.33882152 0.2171424
#>
#> $`152`
#> times CIF1 CIF2
#> 1 5.133665 0.0000000 0.00000000
#> 2 5.200000 0.0517717 0.00000000
#> 3 5.700000 0.1357406 0.00000000
#> 4 6.200000 0.3195265 0.00000000
#> 5 6.700000 0.3195265 0.00000000
#> 6 7.200000 0.3195265 0.06007945
oldpar <- par(mfrow = c(2, 2), mar = c(5, 4, 4, 4))
plot(survfit, include.y = TRUE)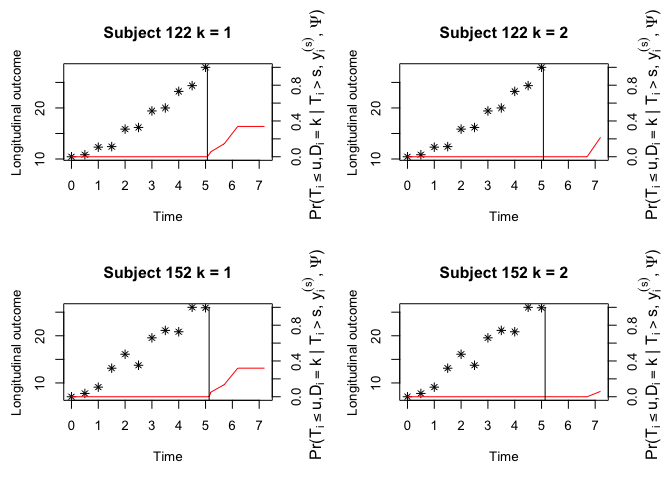
par(oldpar)If we assess the prediction accuracy of the fitted joint model using
Brier score as a calibration measure, we may run PEJMMLSM
to calculate the Brier score.
PE <- PEJMMLSM(fit, seed = 100, landmark.time = 3, horizon.time = c(4:6),
obs.time = "time", method = "GH",
n.cv = 3)
#> The 1 th validation is done!
#> The 2 th validation is done!
#> The 3 th validation is done!
summary(PE, error = "Brier")
#>
#> Expected Brier Score at the landmark time of 3
#> based on 3 fold cross validation
#> Horizon Time Brier Score 1 Brier Score 2
#> 1 4 0.06369906 0.06194668
#> 2 5 0.10838731 0.11052099
#> 3 6 0.20187572 0.11613515An alternative tool is to run MAEQJMMLSM to calculate
the prediction error by comparing the predicted and empirical risks
stratified on different risk groups based on quantile of the predicted
risks.
## evaluate prediction accuracy of fitted joint model using cross-validated mean absolute prediction error
MAEQ <- MAEQJMMLSM(fit, seed = 100, landmark.time = 3,
horizon.time = c(4:6),
obs.time = "time", method = "GH", n.cv = 3)
#> The 1 th validation is done!
#> The 2 th validation is done!
#> The 3 th validation is done!
summary(MAEQ)
#>
#> Sum of absolute error across quintiles of predicted risk scores at the landmark time of 3
#> based on 3 fold cross validation
#> Horizon Time CIF1 CIF2
#> 1 4 0.386 0.262
#> 2 5 0.476 0.346
#> 3 6 0.456 0.430Using area under the ROC curve (AUC) as a discrimination measure, we
may run AUCJMMLSM to calculate the AUC score.
AUC <- AUCJMMLSM(fit, seed = 100, landmark.time = 3, horizon.time = c(4:6),
obs.time = "time", method = "GH",
n.cv = 3)
#> The 1 th validation is done!
#> The 2 th validation is done!
#> The 3 th validation is done!
summary(AUC)
#>
#> Expected AUC at the landmark time of 3
#> based on 3 fold cross validation
#> Horizon Time AUC1 AUC2
#> 1 4 0.5502137 0.6839226
#> 2 5 0.6182312 0.6523506
#> 3 6 0.6103724 0.7065657